AMS: Data Collection Service
Introduction
This is the second article in my Application Monitoring System (AMS) series where I am building an open source application to monitor performances of other applications. In this post, I will be discussing about the second component, the Data Collection Service.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Data Collection Service
- The API page
- DataCollectionConfig
- Config operations
- Data collection
- Conclusion
Data Collection Service
The Data Collection Service is a Spring Boot application written in Java. As the name suggests, it is the collector component of our Application Monitoring System and it has the ability to pull metrics data from various source systems and send to various destination systems.
The API page
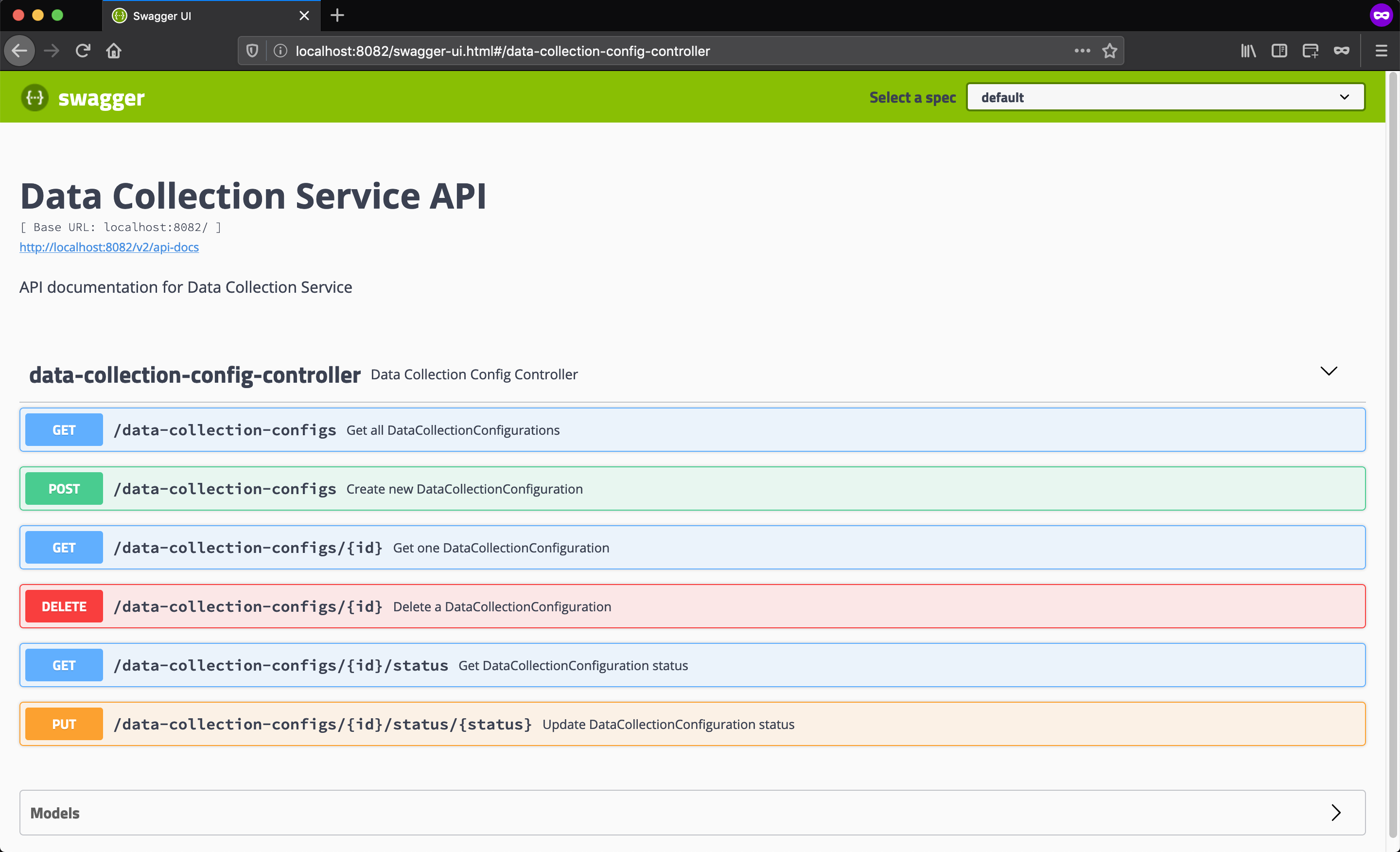
The Data Collection Service does not have a traditional UI. It exposes a set of REST APIs for various administrations and configurations related tasks. It uses the Swagger API Documentation tool to generate a webpage that lists all the REST APIs and the best part is that the REST APIs can be tried directly from the webpage.
The API page uses the default URI for Swagger UI which is /swagger-ui.html. This URL and the all other REST URLs of the Data Collection Service are protected by a basic authentication. The default username is admin and the password is also admin although it can be configured to use something else. Once you go past the authentication page, here’s how the API page looks like:
DataCollectionConfig
A DataCollectionConfig contains the required details for the Data Collection Service to start collecting data (metrics) from a source system and push to a destination system. One Data Collection Service is capable of collecting data from multiple source systems and publishing to multiple destination systems.
Source configs
Although the Data Collection Service includes a flexible enough framework which is capable of supporting data collection from various source types and also publishing to multiple destination types, currently it uses a polling based mechanism for data collection and only the applications exposing the Spring Boot Actuator APIs like the Data Provider Service are supported.
A SourceConfig specifies the source system details within a DataCollectionConfig.
Destination configs
Currently only pushing data to a MongoDB database is supported but in future Data Collection Service is also going to support publishing data to a Kafka stream. While the destination type can be selected in a DataCollectionConfig, the destination system details are not exposed and it is not user-configurable.
Here’s how a complete DataCollectionConfig looks like:
{
"id": "an-auto-generated-uuid-value",
"description": "An arbitary user input field",
"destination": "Database",
"source": "SpringActuator",
"sourceConfig": {
"pollInterval": 60,
"protocol": "http",
"ipAddress": "source-ip-address-or-hostname",
"port": 8080,
"userName": "admin",
"password": "admin"
}
}
Config operations
Several DataCollectionConfig operations are supported by the Data Collection Service REST APIs. Here’s a list of supported operations.
Store
A DataCollectionConfig can be created or updated. If the payload DataCollectionConfig contains the id field, then the existing DataCollectionConfig with the input id is modified with the new values, else a new DataCollectionConfig is created with an auto generated id.
Retrieve
DataCollectionConfigs can be searched by ids or they can be retrieved as a collection.
Remove
DataCollectionConfigs can be removed from the database by their ids.
Data collection
Although the data collection is started as soon as a DataCollectionConfigs is added to the Data Collection Service and stopped when it is deleted, REST APIs are available for monitoring or administering the data collection status for a DataCollectionConfigs.
Conclusion
The source code for the Data Collection Service can be found here. While the Data Collection Service does not support most of the source and destination system types yet, with it’s loosely coupled and pluggable source processor and destination processor pipeline, it can be easily enhanced to support additional array of protocols and systems.
In the next post, I will talk about the next component which is the Data Streaming Service and pushing data from the Data Collection Service to the Data Streaming Service.