Installing qemu with kvm and virt-manager
I have used Oracle Virtualbox before. It has an easy and intuitive UI, supports all the features I needed and is open-source. But this time I decided to use another widely recognized virtualization solution on Linux, qemu, along with kvm.
First of all, let me give some brief idea about qemu, virt-manager and kvm. Qemu is the software which can be used to install and run a guest OS on top of the actual OS to put it in a very simple way although it's much more powerful than that. It can be compared to Virtualbox except that qemu itself does not have a UI, instead it's a command line utility. Virt-manager is some thing that provides a GUI to qemu. Together virt-manager and qemu can be thought of as the Virtualbox. On the other hand, kvm is the Linux kernel module that can help qemu execute the virtualized instructions directly on the CPU which can improve the performance greatly. This is to be kept in mind that qemu can run even without kvm but the speed will be much slower.
The system that I have comprises of an AMD Fx6300 processor with 6 cores and AMD-V capability and 4 gigs of RAM. AMD-V is similar to Intel vt-x and it enhances the virtualization capability of a processor. I am running Xubuntu 14.04 as my main OS with Linux kernel 3.19.0-56 64 bit at the time of writing.
First of all, I needed to enable the AMD-V from the BIOS menu to take full advantage of the processor. For my system, the option could be found in BIOS Settings > Advanced BIOS Features > Virtualization. I just had to enable the flag. After that, I restarted the system and logged into my computer. I installed the following packages:
sudo apt-get install qemu virt-manager virt-viewer libvirt-binI didn't install the qemu-kvm package as this package is not needed for a x86_64 hardware.
To install on Debian 10, following commands should be used.
#Install the required packages.
sudo apt install qemu-kvm libvirt-clients libvirt-daemon-system virt-manager
#Required to create and manage vms without root. <user-name> should be replaced with actual user name.
sudo adduser <user-name> libvirtAfter I restarted the system, I launched the Virtual Machine Manager and it looked like this.
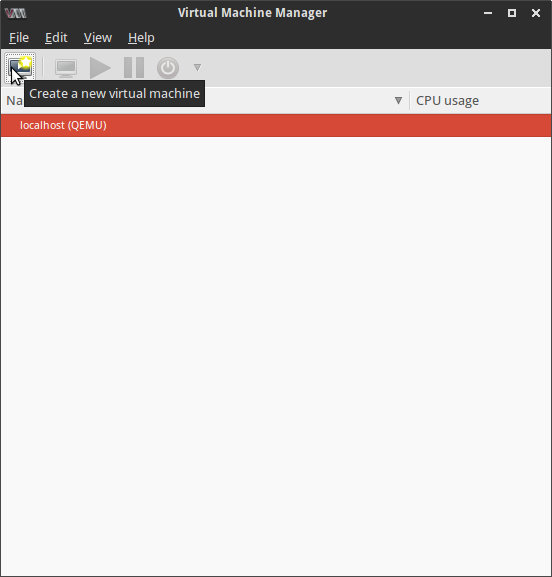
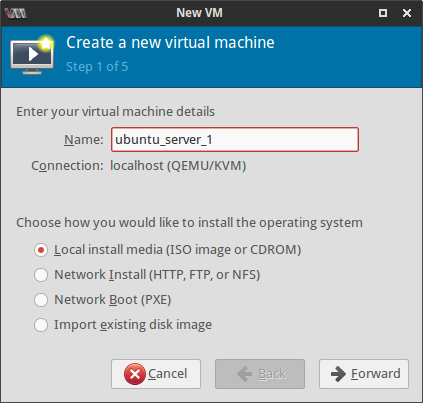
Next few screenshots quickly show the steps of creating and launching a new VM where I had to provide a name for the VM, select the installation CD image and specify the amount of RAM, number of cores and the size of the hard disk image for the virtual machine.
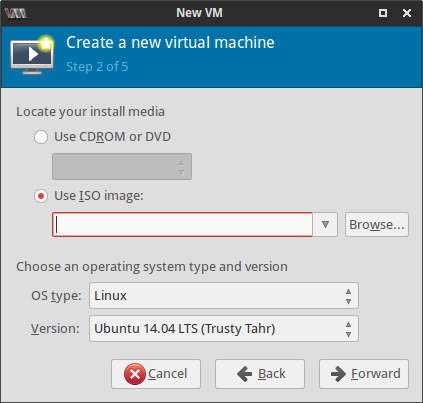
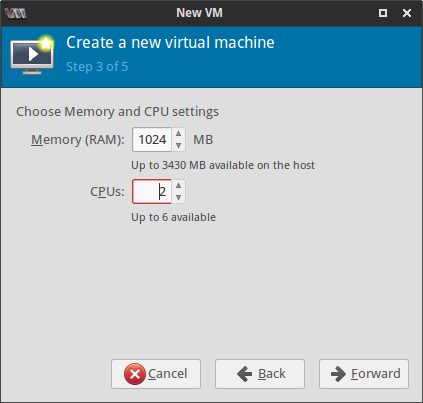
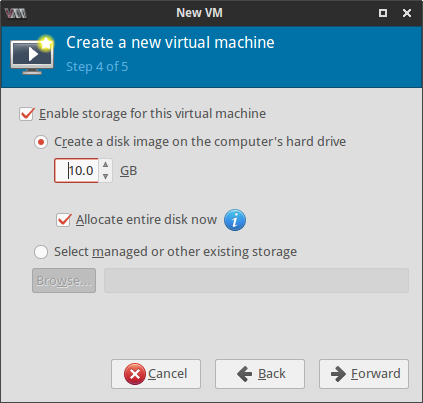
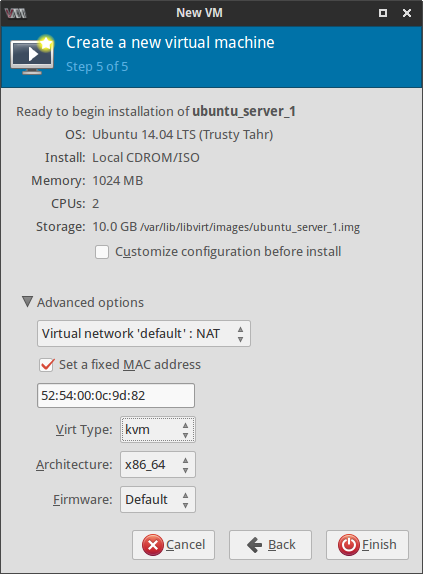
I selected the Virt type as kvm to take advantage of the virtualization capabilities of the Linux kernel. After clicking on the Finish button, the VM is launched with the selected ISO image in the second step. Well that's about it. Pretty easy, I would say!
The advantage of using qemu + kvm over Virtualbox is that it does not require me to install any additional module in the kernel. I haven't taken any benchmark of the performance though. If you have any suggestion/correction please let me know in the comments.